The study highlights the importance of emotional concerns in design, specifically in the process of innovation. While some design scholars have explored the relationship between emotions and design from users’ perspectives, few of them have focused on the changes in junior design students’ emotions during the innovation process.
Project Introduction
The study highlights the importance of emotional concerns in design, specifically in the process of innovation. While some design scholars have explored the relationship between emotions and design from users’ perspectives, few have focused on the changes in junior design students’ emotions during the innovation process.
Project Aim
This study aims to explore how emotions can be effectively integrated into design education and to propose a new approach for design studies based on emotional guidance.
Project Objectives
The objectives of the study are to understand the emotional changes that junior design students experience during the innovation process, to analyse the effects of emotional guidance on design outcomes, and to explore the possibilities of incorporating emotional guidance into design education.
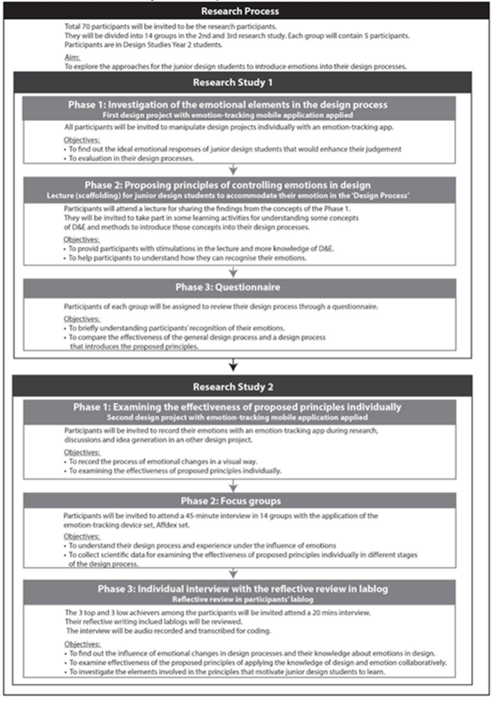
Research Method
- The study used a mixed-methods research design, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews.
- The quantitative survey was conducted to collect data on the emotional changes that junior design students experience during the innovation process.
- The qualitative interviews were conducted to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of emotional guidance on design outcomes and to explore the possibilities of incorporating emotional guidance into design education.
Concept Model
Findings
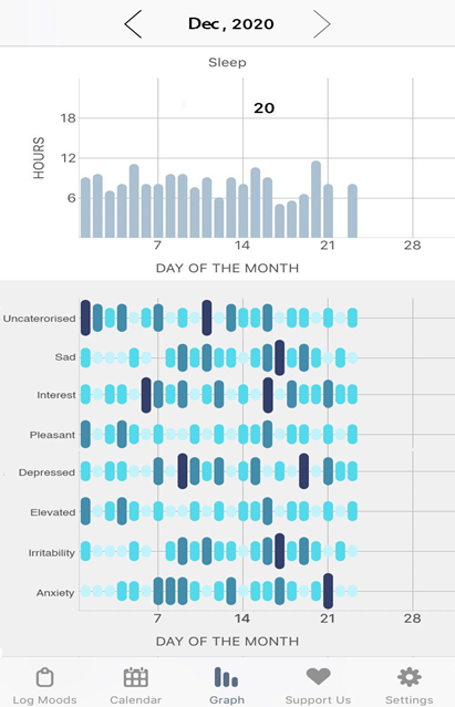
- Participants were able to recognise some basic emotions through the eMoods application. Participants identified anxiety, irritability, interest, and pleasantness, but did not indicate emotions such as depressed, sad, elevated, or uncategorised.
- The eMoods application was effective in identifying potential problems for design practices and pinpointing optimal emotional reactions of junior design students that would improve their ability to make decisions throughout the design process.
- Participants had difficulty recognising detailed emotional changes from one particular emotion to another and were not sensitive to their emotional changes during the design process.
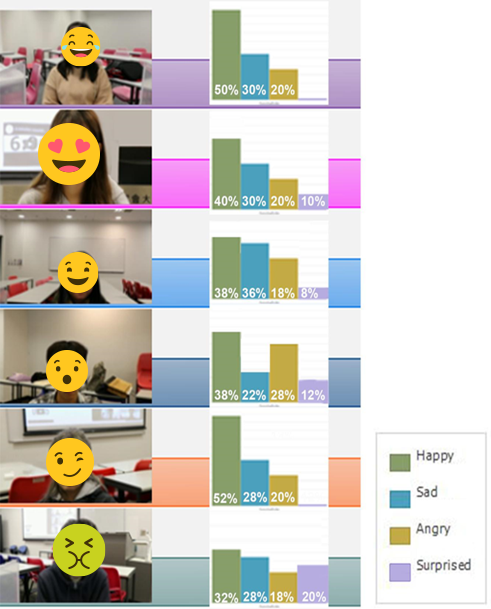
- Emotional adjustment speeds may influence the management perception between designers and emotional stimulus, which may impact decision-making and the manipulation of the design process. Negative feelings such as anger and sadness can decrease the ability to carry out design solutions.
- Emotional shifts may influence designers’ personal perceptions, decision-making, and the manipulation of the design process. Inefficient decision-making and design process difficulties increased when the participants obtained relatively negative emotions.
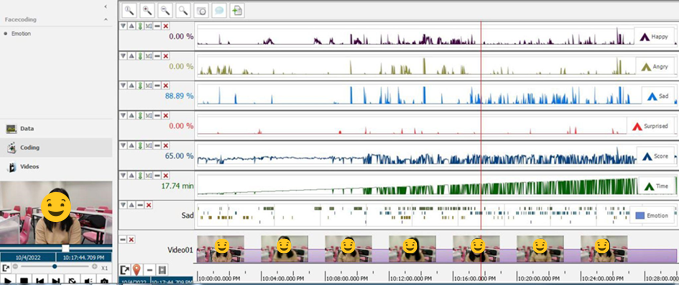
- Emotional tracking had an obvious effect on the design process and outcomes. The collected data would convince designers to introduce emotional concerns into their design process, as well as provide relatively accurate and obvious information on emotional changes.
Deliverables
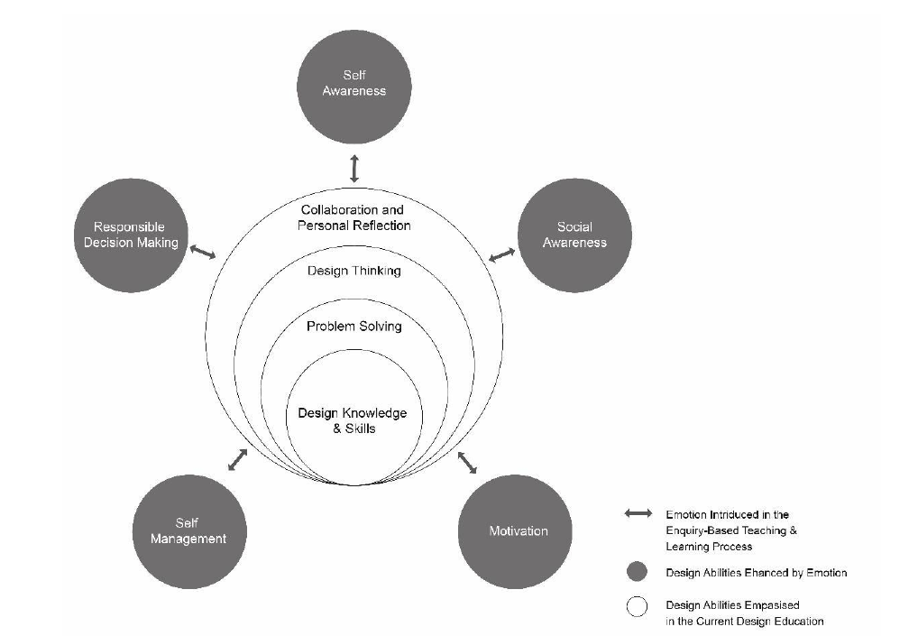
The Emotion-guidelines were proposed to provide guiding principles to assist Junior design students/art and creative students in regulating their emotional changes during the design process. This is significant as it is the first time that the concept of ‘design and emotion’ has been incorporated into the study of the design process.
Connecting Emotion with Design Learning.
HO, A. G. (2023). In: Kye, H. W.; Kim, D. W.; Kim, S. M.; Kim, E. R.; Park, J. H.; Lee, J. Y. & Choi, J. M. (eds) Proceedings of the HCI Korea 2023 (한국 HCI학술대회 2023). (pp. 586-592). Gangwon-do 강원도, South Korea: The HCI Society of Korea.
Emotion from Creativity: Principles of Manipulating Emotional Management in Design Learning.
HO, A. G. (2022). In: Bruyns, G. Wei, H. (Eds) [ ] With Design: Reinventing Design Modes. IASDR 2021. (pp. 276-290). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4472-7_19
Understanding Junior Design Students’ Emotion During the Creative Process.
HO, A. G. (2021). In: Ayaz H., Asgher U., Paletta L. (eds) Advances in Human Factors in Training, Education, and Learning Sciences. AHFE 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 269. (pp. 120-126). Springer, Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80285-1_15
The Emotion Guideline: Workbook for managing your Emotions in the Design Process.
HO, A. G. (forthcoming).Florida, USA: CRC Press Taylor & Francis.
Guiding Emotion: Constructing New Approach for Design Studies.
HO, A. G. (forthcoming). Florida, USA: CRC Press Taylor & Francis.
Funded Sources
Competitive Research Funding Schemes –
Faculty Development Scheme Project (FDS) Research Grants Council, University Grants Committee (UGC) Hong Kong
Project Reference No.
UGC/FDS16/E06/19
Period
01 Jan 2020 – 31 Dec 2021
Funded amount
HKD 580,000
Principal Investigator:
Dr HO Amic Garfield (HKMU)
Research Assistant:
Ms CHAU Pui Wa (HKMU)